Online automotive marketing course
Automotive Design & Marketing Management
We are dedicating these last two posts to see what happens once the car leaves the factory. In the previous post we focused on what happens in design centers, and in this one we will focus on the commercial network. As we discussed in the previous post, at the training level, distribution is not usually connected with automotive design, each one goes separately. The same happens with professionals in the sector, each one is an expert in their area, but without knowing the rest of the stages of vehicle development. This results in great designers and engineers but who do not know in depth the whole automotive sector, and it is a shame, because the key aspects of the distribution can be summarized in a couple of installments, and it will be enough to give us a good overview and an understanding of how the automobile business works. How are we going to design and develop cars without knowing how they are sold? This will be the last post to end the cycle and in the next post we will see a summary of everything we have seen, briefly.
Operation of the Commercial Network
Operation of the Automotive Commercial Network
Remember that we are going to study the part that is useful for an automotive designer or an engineer.
As designers, we would make a fatal mistake if our vision were so short that we limited ourselves only to thinking about the vehicle in isolation; since car production is only part of the business, and sometimes, it is not the most profitable. As we saw in the delivery of the trends, previously the car was designed in isolation, but now to try to offer a mobility solution we think about the ecosystem around the vehicle. Therefore, the designer of the future is required, in addition to designing the car, to be able to design its environment, that is, to propose a mobility solution. Having this knowledge is what will give the designer the advantage to differentiate himself even from designers with more years of experience. Vehicle manufacturing is essential to keep the rest of the business branches active. Manufacturers determine three types of profit: gross profit, operating profit, and net profit. Gross profit is the difference between the cost of making the vehicle and the price at which it is sold. It is estimated that brands such as Toyota and Ford earn an average of € 1,600 per car sold, with no extras. These profits are not enough to justify the large outlays of the brands in R&D or in advertising. In fact, there are manufacturers who lose money when they sell a car. Brands like PSA and Renault are estimated to lose between 1% and 4% of the car's value, with no extras, of course. In the next point we will see one of the secrets of the automotive business.
Premium brands have a higher gross profit than conventional brands per model sold. In a luxury market, the profit margin tends to increase, but the volume of units manufactured is lower. The opposite happens with conventional brands, higher volume at a lower profit margin. This is why many convetional brands have an associated premium brand (DS for Citröen, Cupra for Seat, etc.). This point has to be controlled by the designer, since he will have to offer the brand a correctly positioned vehicle on the market with a production volume that is profitable for the brand.
How do car brands make money?
At this point we are going to see how car manufacturers make money, but we will continue to discover more in the next point when we see how an official dealer of the brand makes money, since both points are directly related.
These are some of the alternative ways that a brand has to generate income in addition to the sale of vehicles and spare parts:
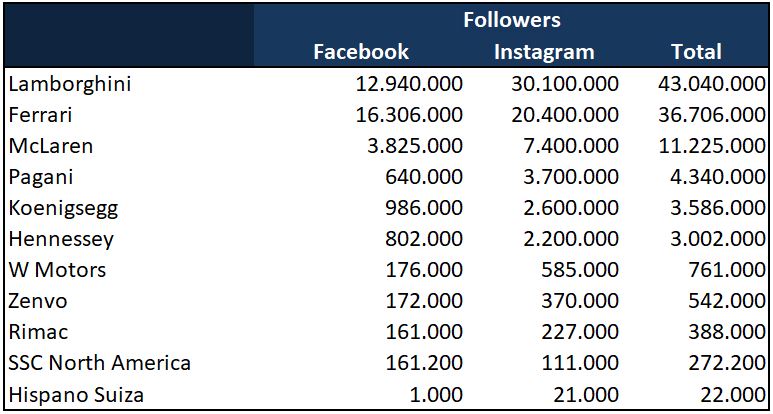
For merchandising it's essential to create a strong brand image. Ferrari is the reference in this, it's an economically inaccessible car for most people, but it's a brand close to the public through models, video games and Formula One. This spark the interest from the general public. Also, anyone who walks into a Ferrari dealership is totally welcome, even if you can't buy the car. Lamborghini also arouses great interest, making it a very appropriate brand to sell merchandise. Lamborghini pays special attention to children, as these will be the ones who will buy a Lamborghini in the future. It's a very long-term strategy but with excellent results. They know how to maintain proximity to the people and the exclusivity of the brand. This makes the general public like these brands, even if they cannot buy them. Brands have to keep a balance. For example, brands that are too generic and inexpensive don't tend to generate enough interest to have a strong merchandising line, while a dream car brand can stray too far from the generic audience. Social networks can give us an idea of the popularity of a brand, although there are many other factors to take into account, but it gives us a general idea. We are going to only compare some brands that manufacture super-sports cars to be on equal terms. We see that, although Ferrari is in Formula One, Lamborghini's long-term strategy puts it in first position. Despite the fact that Ferrari takes excessive care of its brand image. It's interesting to see that Hispano Suiza, despite having more than 100 years of history, many economic resources and a fascinating super sports car on the market is hardly popular. But everything has a meaning when we analyze it. Hispano Suiza is much less popular than more recent brands. Due to the history of the brand, it should be in positions close to Pagani and Koenigsegg. This is because Hispano Suiza completely rejects anyone who doesn't belong to the bourgeoisie, categorically. In a car show you can freely ask about any of these brands, except for Hispano Suiza, you would be completely ignored and rejected. In this way they manage to be a super-exclusive brand in all dimensions. It's a different strategy from the others and radically differs from the rest of exclusive and expensive brands by categorically rejecting common people. In this way, it doesn't focus only on a wealthy client. But on a very exclusive and specific type of bourgeois client, thus it sparks interest only in its target audience.
Structure of the Commercial Network
Structure of the automotive sales networkHere we have two key elements: Headquarters: It's in charge of the operational part. Let's take BMW as an example. The headquarters is usually in its country of origin, Germany. But later in each country we find another headquarters that is in charge of managing the commercial network in that country or region. The latter ones negotiate the main goals with the brand, then divide and distribute these objectives to each dealer, studying their different capabilities. In other words, the headquarters in Spain would negotiate with Germany the targets for Spain, and then the brand diversifies the work among the different dealerships in the country to achieve the goal. The headquarters of each country also ensures that the network meets the standards of the brand, they ensure that the staff has the necessary training, they provide the marketing material, including digital marketing and visual merchandising, they develop the strategy. commercial (incentive plans, loyalty programs ...) , etcetera. They don't take part in design and development, at most, they offer statistical data for marketing or collaborate in some special edition. But as a general rule they don't take part in development engineering. The distribution network: Mainly made up of dealers and services. The commercial network is not exactly the same in all countries, so it may show certain variations. In addition, the following point will explain the traditional dealership model, but this model is currently undergoing an important digital transformation. Currently a client can carry out up to 80% of the purchase process online. This process begins from the search for vehicle information, currently people can do it online, but it was not like that just a few decades ago. Let us remember that cars are designed for the future. At first glance it seems that this doesn't influence the design. But for example, as a designer we could justify an increase in the cost of higher quality materials that will be offset by savings made as a result of lower expenses derived from the traditional sales model. Currently there are brands that are trying to sell online, trying to keeping some facilities open only as a showroom. Digitization doesn't end here, but Big data and Cloud Computing allow us to collect and synthesize in a better way all the data to obtain conclusions that help us design our commercial strategy.
Car dealership business model
Car Dealership business modelWe will discuss how a car dealership works from the designer's point of view, worrying only about what is useful when creating a new product. Normally a dealer doesn't belong to the brand, they work for concessions. In other words, an independent entrepreneur or business group owns several dealerships that can operate for different brands, even if they are competing brands. So it's possible that in the same facility sells a brand and ,over time, interests change and move into selling one of the competitors. This operation is really expensive for the business group and requires a lot of time, so it isn't usual, but it's possible. This fact is important because it implies that the brand doesn't usually have proprietary dealerships, but rather grants concessions to different business groups. In fact, in the United States, a car manufacturer cannot own a dealership, which is one of the reasons why Tesla had to force it to sell online, since the facilities where they display their cars are their property. It should be noted that many brands do have dealerships owned outside USA, but it's usually a small number of facilities and in key locations. The expansion of the brand in the country is carried out through concessions to increase the number of points of sale. It must be borne in mind that, usually, to be an official dealer it must first be an official service, that is, a workshop approved for the brand. Being approved by the brand implies, among other things, having to acquire a specific workshop equipment from the brand, pass its quality controls and train the mechanics team again to certify it by the brand. If a dealer doesn't meet the standards, they may lose their brand concession and the right to sell their vehicles. This business group will also be able to set its own incentives and marketing strategies in a complementary way to those established by the brand. Do dealers buy their cars from the manufacturer?Very few dealers have enough cash flow to acquire so much stock, instead, we always find them full of the latest models. How do they have so much money to have all that immobilized stock? The vast majority of dealerships pay a rental to the manufacturer to have the car at the dealership ready to sell. This movement is carried out under a type of financing called “Floorplan”. This is an economic income for the manufacturer, we didn't show it previously so as not to reveal it ahead of time. But there is still more to discover, in fact, now comes the interesting thing.
How does a car dealership make money?
How does a car dealer make money?We saw in the previous point that a car brand doesn't make money only by selling its cars, in fact, sometimes they have a really low profit margin per car sold (when talking about basic models). If we're going to design a car, it's very advisable to understand how the automotive business works, otherwise it will be difficult to create real proposals. An important part of the profits of a dealer doesn't come from the sale of new vehicles, but from different services:
1º - Financial services:
We will see it in the most enjoyable way possible, I promise. This includes financing, insurance, and maintenance plans. A manufacturer that has its own financial institution has a clear advantage over other brands that only have agreements with external financial institutions. In this way the brand obtains an extra capacity to generate money for the business. We're going to explain it in the most pleasant way possible, so we aren't going to go into details, in addition, this information is easy to obtain. So we're going to focus only on what interests us for the product strategy of a car brand. There are currently three additional ways to market a vehicle that should be highlighted:
1st way - Financing: On the one hand, the client contributes a down payment, and then the entity finances a part of the value of the vehicle. In this way, the client pays a really small monthly fee, which is the one that is financed. So he perceives that he is paying little for his vehicle.
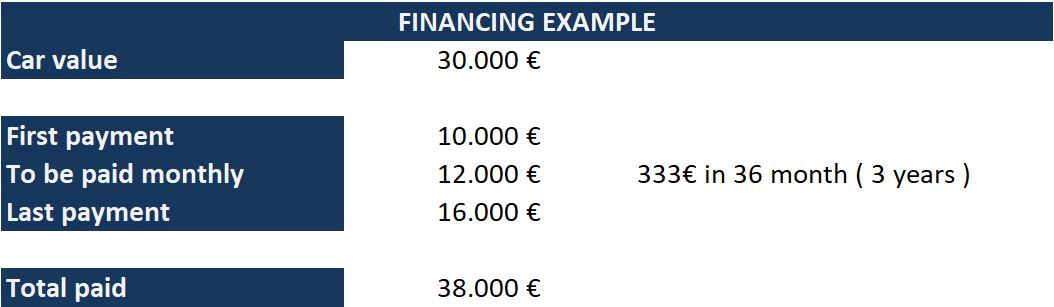
In addition, the financial institution has greater liquidity since it doesn't need to finance 100% of the value of the customer's vehicle but only a fraction of its value. This allows it to close a greater number of operations with the same capital. That is, we can sell more cars with the same money. In addition, the finance company has a fairly accurate forecast on the incoming capital month by month, something really advantageous in business. It's much better to know your income with precision from month to month, than to base yourself on an estimate. This is because every month there is a fixed number of clients paying a monthly payment. For example, if we have a € 30,000 car, the client can give a down payment of € 10,000, and pay a monthly amount of money in easy installments, which will generate additional interest. After three or four years, the client can decide if he want to finish paying for their vehicle, in that case, they will pay the entire remaining amount, which would be € 16,000 in this example. If the customer decides not to do, he can stop paying and return the car, or he can exchange his car for a current model and continue to pay the monthly fee. In this way, the customer's monthly payment commitment is maintained, a new vehicle is registered and the dealer obtains a second-hand car to add to his stock. Let's see the game, we have gone from selling a car of € 30,000 for a higher amount due to the gain of interest from the financing, and the client perceives that he is paying less. That is, in addition to the profit from the financing, we're getting a customer to access a € 30,000 car with only € 10,000, something that seems like a bargain for the customer. The brand increases the sales volume, in addition to gain stock of second-hand cars that are only three or four years old. We saw previously that the marketing had an impact on 25% of the final price of the model, without taxes. As an additional advantage to this strategy, we save vehicle marketing costs, since many of the sales will go directly to people who are already customers, so we don't have to spend money on marketing and it helps us a lot to make a sales forecast. This is one of the keys to the automotive business, curiously, the sales model is much more public information than that shown in other posts, but it isn't usually connected with car design/development or with its product strategy. The fees are usually very small so that the client is paying little by little, so it is a great commercial claim. Four years after purchasing the car, the customer is not as excited as the first day. Then suddenly there is a last payment that is usually close to 50% of the price of the car, then the customer tends to choose not to pay it. This last payment is directly related to the residual value, that is, the value of the car in the second-hand market after those four years. At that moment is when the salesman comes into action and shows you the latest model, then it gives you the option to continue paying those "comfortable" installments and start using the latest model. Curiously, the client doesn't even remember the € 10,000 that he invested four years ago and will continue to pay monthly without ever owning the car if he decides to continue renewing it. This is product strategy at its best. We will see later why this benefits the brand.
2nd Way - Renting: The dealer offers the vehicle for rent for several years. Once the contract time ends, the dealership will try to retain the customer, offering him a new model within the same line to renew the renting contract. In this way, the customer always enjoys the latest model without having to pay a large amount for the vehicle. The dealer has a constant capital inflow. At the end of the renting, the dealership may also add a used car to their stock that they have maintained themselves. In the same way, the financial company of the brand also obtains profitability in this process.
The customer doesn't have to worry about maintenance costs, insurance, roadside assistance, etc. This modality is intended for freelancers and companies, although anyone can purchase a rental car. It's a great advantage for companies that hire the service because they don't have to worry about vehicle maintenance. In the event of any problem, they leave it at the dealership and take a replacement car, so the company can continue to operate without problems. In addition, it's a tax deductible service for companies and freelancers. Currently there are small car brands that are designing cars only for renting, so they will not be vehicles owned by the client. 3rd Way - Leasing: It's a kind of rental contract with an estimated duration. In this case, the lessee is responsible for all the expenses of the vehicle. Unlike renting, at the end of the rental period, you have the option of buying the car by paying its residual value. In other words, it is a rent with option to buy. The tenant of the vehicle can also choose not to acquire the vehicle and end any type of financial relationship with the brand, or can extend the leasing contract to be able to enjoy the latest model on the market. Something similar happens that with renting, the dealer and the financial company of the brand ensure a constant inflow of capital, and in turn, the brand will add a second-hand car to its network of dealers. In short, whatever the option, the intention is always the same: Make the car accessible to the customer, manage to "sell" a new model to the same customer after four years and add a used vehicle with a few years. Here we begin to see the importance of the next car design and restyling.
2º - After-sales services
We have seen before that the first way to make money was with financial services. The second way to earn money for a dealership is based on after-sales services. In this part it's important to know how to encourage client loyalty. Workshop: Vehicle maintenance and repairs. In the workshop part, it's important to have agreements with insurance companies and rent-a-car companies. On the other hand, it's important to retain your customers to get them to go to the dealer's workshop instead of to independent workshops. The head office usually carries out promotions or incentives when goals are achieved, allowing the dealership to make discounts and promotions to its customers to attract them. In the same way, the mechanical guarantees offered by the manufacturer to consumers ensure an increase in workshop steps and greater customer loyalty, although with a lower profit margin for the dealer. After-sales: Another important branch of the after-sales business is the sale of vehicle accessories and spare parts. This can be even 50% of the profits in some dealerships, mainly due to the sale of spare parts; something that also makes the manufacturer money. Here we're going to see an important fact. A dealership is free to purchase an original part or a compatible part supplied by another supplier. That is why many parts are exclusive to the manufacturer itself, so that there are no other external suppliers that manufacture them on their own. These parts can only be purchased at dealerships or official services of the brand. This part of the business ensures a cash flow directly to the manufacturer. Although in turn, it's detrimental to the relationship with the insurance companies since, in the event of an accident, they must purchase an original part at a higher cost. In other words, the greater the number of original parts, the more expensive the car insurance will be. This is something that is important to potential buyers. So it can affect final sales. The spare parts stock turnover rate is very important in the business. A dealership has to correctly predict which parts to order in advance to be able to offer a spare part quickly to the customer, but without it becoming obsolete. The dealership will always have to maintain a minimum stock in his facility according to the requirements of the brand.
3º - Reaching the goals
The headquarters incentivizes dealerships with different programs. If the dealership achieves the objectives, the headquarters incentivizes them financially. If a dealership is close to meeting the objective but is running out of time to achieve it, it's profitable for them to sell at the minimum price to achieve the objective and obtain a capital inflow greater than the own profit that they would have obtained by selling the product to their usual price. Although this applies in all areas of the automotive business, we see a clear example in the self-registrations of cars. Self-registration of a car is when a dealer sells the car to itself, absent a buyer. This is done to meet the registration fees imposed by the brand. These vehicles are also used by the dealership for customer test drives, courtesy or replacement vehicles, and for employee use. They are also offered for direct sale as "0 kilometer vehicles".
4º - Purchase and sale of used cars
We have business here! . Most of the official dealerships offer both new vehicles and second-hand vehicles. A used vehicle usually enters the stock of a dealer in four different ways: Buy-sell: When a customer purchases a new car and gives his old car as part of the payment. This operation is usually quite profitable for dealers. Remarketing: This is a really important part because it has completely changed the car business model. One of the most relevant aspects in recent years is the sale of fleets. These fleets are usually sold to renting companies. Although in recent years a new player has been added to the scene: car-sharing. The brand negotiates with different companies a sale price and a buyback price after a short period of time, which ranges from 6 months to 2 years. The difference between both costs is called the “holding cost”. All the terms of the contract are stipulated. The buyback price will vary depending on the condition in which the car is returned and the final mileage. During that time, the company that acquires the fleet undertakes to carry out a thorough maintenance of the vehicle. The smart move is to agree with these companies that vehicle maintenance is carried out in your own network of dealerships and official services. This means higher profits and greater control of cash flow. After that time, these vehicles will be repurchased by the manufacturer itself and will become part of the brand's commercial network to be sold as brand-certified used vehicles. This is a really important part of the automobile business. It's widely known by any salesman in the sector, but unknown by many automotive engineers and designers. When companies rsell their fleets to brands, it's called “De-Fleet”. The brands then recondition the cars to sell them at the best cost. Leasing / Renting: As we saw previously, when a rental contract expires, the car goes to the dealer network. In leasing the customer has the option to buy the car, but if he doesn't do so, the dealer will add a new second-hand vehicle to his stock. Used car auctions: Some dealers choose to participate in this type of auction to add cars to their stock. This happens especially in multi-brand dealerships that don't belong to the commercial network of a manufacturer. This doesn't imply profit for the manufacturer.
Planned Obsolescence
When we talk about planned obsolescence we're not talking about reducing quality. That is, we're not talking about manufacturing products that fail after a few years reducing their useful life. But to manufacture technological products that leave their predecessors out of date. So far we have talked about the commercial part, but, Why is it important for a designer to know these concepts? Remember that the time to design a car is about five years. These times tend to be shortened using existing platforms. But there is also another interesting strategy to fictitiously shorten these times: The restyling. We are all familiar with this term, but its relationship to product strategy is rarely studied. Whether in remarketing, leasing or renting, the vehicles return to the brand's commercial network after time, between 6 months and 4 years. Nowadays, a brand doesn't only have to worry about selling new cars, but about reselling its own used cars. This, which seems basic, completely changes the landscape of car design. When designing the vehicle, its obsolescence must be carefully studied: Imagine that four years after buying a new car, it seems out of date. Then the residual value of the car after those four years would be too low and the brand would obtain a low profitability when trying to sell it second hand. A vehicle with an aesthetic design too in line with a fad may look out of date after a few years, and the customer will perceive it as an older car than it really is. Then the customer will be willing to pay less for it. Therefore, for a vehicle to easily become outdated is very negative for the manufacturer as the second-hand car business is also being a significant source of income. In addition, the emotional component is also added, no person wants to buy a car that looks old at four years, that would give a bad brand image. The same will happen if we are able to design a car that dazzles its predecessor, improving it in everything. In this case we are facing the same situation as above. It will be very hard for the brand to sell the second-hand model because the new one will be better in all aspects. We're interested in keeping the residual value as high as possible, that is, that the depreciation of the model is low so that it doesn't lose much value in the second hand market. Earlier we just saw two cases where the cars was out of date. Now let's go now to the opposite case: If we design a car in 2016, and then in 2020 we design another that hardly shows any changes. In this situation, all customers will keep their 2016 car because they wouldn't see the point in purchasing a new product. If this happens, we lose the second-hand car business as no customer has disposed of their car, and more seriously, no new models would be produced because no customer would want to buy the 2020 model. Therefore, both situations are dangerous. If the new model is too novel, the old one will lose value in the second-hand market. But it's even worse if the new model looks too much like the predecessor. So here we have one of the biggest dangers and opportunities in a car's design strategy: Design something that is a little better than the previous one, but not too much! A new model has to differ from the previous one to justify that customers purchase it, but at the same time, it shouldn't be too differentiated. At the midpoint is virtue. Knowing this, the next design proposal doesn't have to focus on a groundbreaking aesthetic, but can focus on a business model according to future trends. For example, designing a car taking into account its depreciation in four years, and in turn designing the model that will replace it in another four years, using common components to greatly reduce costs. This is part of the automotive product design strategy, the greater the knowledge, the greater the ability to offer a value proposition and not just an isolated concept. Here comes another important aspect of this strategy. Since development of a completely new vehicle takes between three and five years, many manufacturers choose to make minor changes to vehicles through facelift and restyling. At the same time, a new model can be designed in parallel. The facelift: These are minor changes that usually affect the vehicle's technology, either due to the motorization or the vehicle's equipment. The restyling: Affects the aesthetics of the vehicle. It could be a new spoiler, new headlights or bumpers. Remember that each change must be tested, validated, approved. This also affects the supply chain and the assembly line. These developments take much less time and lower costs. It's a smartvway of reintroducing a model to the market or updating it against its competitors. In other words, this product strategy allows us to sell more units, take control of second-hand cars market, have greater control and knowledge of cash flow. It also facilitates the access of cars to consumers, since they don't usually pay the total cost of the vehicle. But it also helps us reduce development times and costs since we're not designing a car from scratch, but we do a restyling or retrofit. With this we conclude this post. We have tried to summarize the entire car distribution business in a single post. These are the key points of the entire car dealership business, fully compressed into one post. Hopefully with this, and with everything shown throughout this automobile course, you have obtained an overview of the entire automobile business. This automotive course has been written from scratch for you with countless hours of work. In addition to professional experience and unpublished material, we have had to investigate much more than expected and consult many professionals in the sector, since no one usually has a 360º vision of the automotive sector. Usually, each expert is in a single field, and is usually unaware of the other fields, especially when we talk about concepts as different as engineering and marketing. But when it comes to car design, it's essential to know the car development from start to finish, even the concepts, and that is what we have tried to teach you. We appreciate your patience with our English level. We're not English native, we are Spanish. We have written the equivalent of 140 pages in English. We remain attentive to any comments or questions you have, we appreciate it very much and they also help us a lot. We would also appreciate any feedback on Google (drivingyourdream) or on Facebook, they help us and motivate us a lot. In the next installment we will see a summary, to have everything fresh. Looking forward to your comments or questions, if you have any. We would also appreciate any feedback on Google (drivingyourdream) or on Facebook, they help us and motivate us a lot. Next post is the last one, but it will be a summary of everything. So this is the last topic in this automotive course that we started six months ago.
1 Comment
3/11/2022 11:05:29 am
Manufacturers determine three types of profit: gross profit, operating profit, and net profit. Gross profit is the difference between the cost of making the vehicle and the price at which it is sold. Nice information thank you so much!
Reply
Leave a Reply. |



















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed